The western fringe of the Devon ice cap on the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The similarity between many Martian valleys and the subglacial channels on Devon Island within the Canadian Arctic motivated the authors to conduct their comparative research. A. Grau Galofre / ASUAccording to new analysis, early Mars was moist, however hardly ever heat.
Ancient Mars probably appeared very very like Antarctica, with ice sheets advancing and retreating throughout its floor, says Anna Grau Galofre (Arizona State University).
Grau Galofre and two colleagues in contrast the shapes of abrasion-lower valleys on Mars with their counterparts on Earth, and in Nature Geoscience they report that a lot of the water that sculpted the Martian floor flowed underneath glaciers — moderately than in floor rivers as had been thought. When the glaciers retreated throughout intermittent heat spells, rivers flowed from the bottom of the ice sheets throughout the floor and lower channels of various shapes.
Switching Course
Decades in the past, maps of the Martian floor revealed networks of channels that seem like river valley networks. The options led many to assume that flowing floor water had formed the panorama of the Martian highlands 3.9 billion to three.5 billion years in the past.
Yet Grau Galofre was not satisfied that floor rivers had flowed freely on a heat and moist Mars. She discovered the reasoning round, as a result of scientists had used fashions primarily based on fluvial circulation to find out how floor channels may have fashioned. Further doubts got here from the shortcoming of three-dimensional local weather fashions to breed a heat and moist younger Mars.
Subglacial flows are an alternative choice to rivers on the floor. And they’re on Earth, too. Those that exist now underneath the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets are largely inaccessible, however the retreat of glaciers from North America on the finish of the final ice age left many subglacial options uncovered, such because the Finger Lakes of western New York. Grau Galofre did discipline work on lesser-identified set of uncovered subglacial channels on Devon Island at 75°N within the excessive Canadian Arctic.
As the world’s largest uninhabited island, it’s a harsh place, and scientists have used it earlier than as an Earth analog for contemporary Mars. With Mark Jellinek (Arizona State) and Gordon Osinski (University of Western Ontario, Canada), Grau Galofre discovered distinctive subglacieal options on the island, together with lengthy, slim parallel branches that come collectively like fingers on a hand.
The three researchers in contrast these options to different water-lower terrestrial channels and developed metrics to categorise 4 distinct kinds of valleys: these fashioned by open-flowing rivers, by meltwater from glacial edges, by sub-glacial flows, and by “sapping” flows originating from groundwater sources. Then they utilized these metrics to hint the origins of greater than 10,000 Martian valleys comprising 66 valley networks — the equal of terrestrial drainage basins.
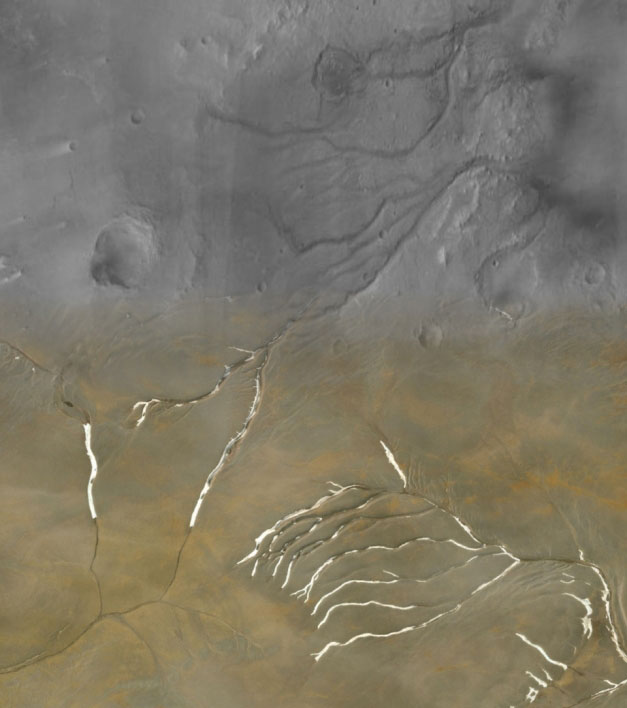
This collage reveals Martian valleys (high) and Devon Island channels (backside). The related form of the channels and the general community is putting.Cal-Tech CTX mosaic and MAXAR / EsriOf these networks, 22 confirmed the hallmarks of fluid erosion underneath the stress of thick glacial ice sheets, similar to teams of finger-like branches separated by lengthy flat areas with few branches. Another 14 valley networks exhibited complicated patterns of tributaries and comparatively slim width of river networks. Nine networks had slim channels 3–5 km (2–Three miles) extensive and different options related to retreating ice sheets, which can overlay subglacial options that fashioned earlier. Only three valley networks appeared like true groundwater flows, although the mannequin couldn’t pin down the origins of the remaining 18 networks.
Life on Mars?
Martian options are dated by counting craters impinging on them, however that is onerous to increase to glaciated areas as a result of we do not understand how properly the impacts would have penetrated the ice. While the age of the valleys isn’t identified, Grau Galofre speculates that they fashioned at totally different instances. The subglacial channels fashioned throughout chilly durations, when water flowed underneath thick ice sheets, ultimately reaching the perimeters of the ice. “When the ice retreated, you would have had rivers,” she says.” But she doubts Mars ever became really warm. Instead, Mars “was all the time just about a frozen world [where conditions changed] from extra to much less frozen, however to not thawed,” she says.
An icy Mars needn’t be lifeless, Grau Galofre says. She factors out {that a} subglacial surroundings would hover across the freezing level for an prolonged time, which might shield any life from dramatic temperature variations in addition to intense photo voltaic radiation. Microbes have lived within the subglacial Lake Vostok, underneath four km of Antarctic ice, for thousands and thousands of years. Perhaps chilly Martian slush would make a very good residence for easy organisms.
Others have instructed non-fluvial origins for Martian channels, however Jeffrey Kargel (Planetary Science Institute), who was not concerned within the research, praises the crew for a “great quantitative analytical approach [that] allowed their interpretation of origins to fall out from the statistical analysis.” He thinks nearer evaluation of the 18 “undifferentiated” networks would possibly reveal that they have been locations the place one course of overprinted the opposite, like outflow from a melting glacier would possibly cowl a channel eroded by subglacial circulation after the glacier had melted.
Yet we’ve barely scratched the floor of Mars in comparison with our detailed examination of terrestrial deposits, leaving many vital questions unanswered. Victor Baker (University of Arizona), who was additionally not concerned within the research, factors out that different phenomena occurring on Mars through the formation of the valley networks are according to heat and moist situations. NASA’s Perseverance rover is now on its option to Mars to discover different elements of its geology that can hopefully solid extra gentle on how heat and moist Mars was in its early days.
Advertisement
Source link