Applications
18/12/2020
2311 views
67 likes
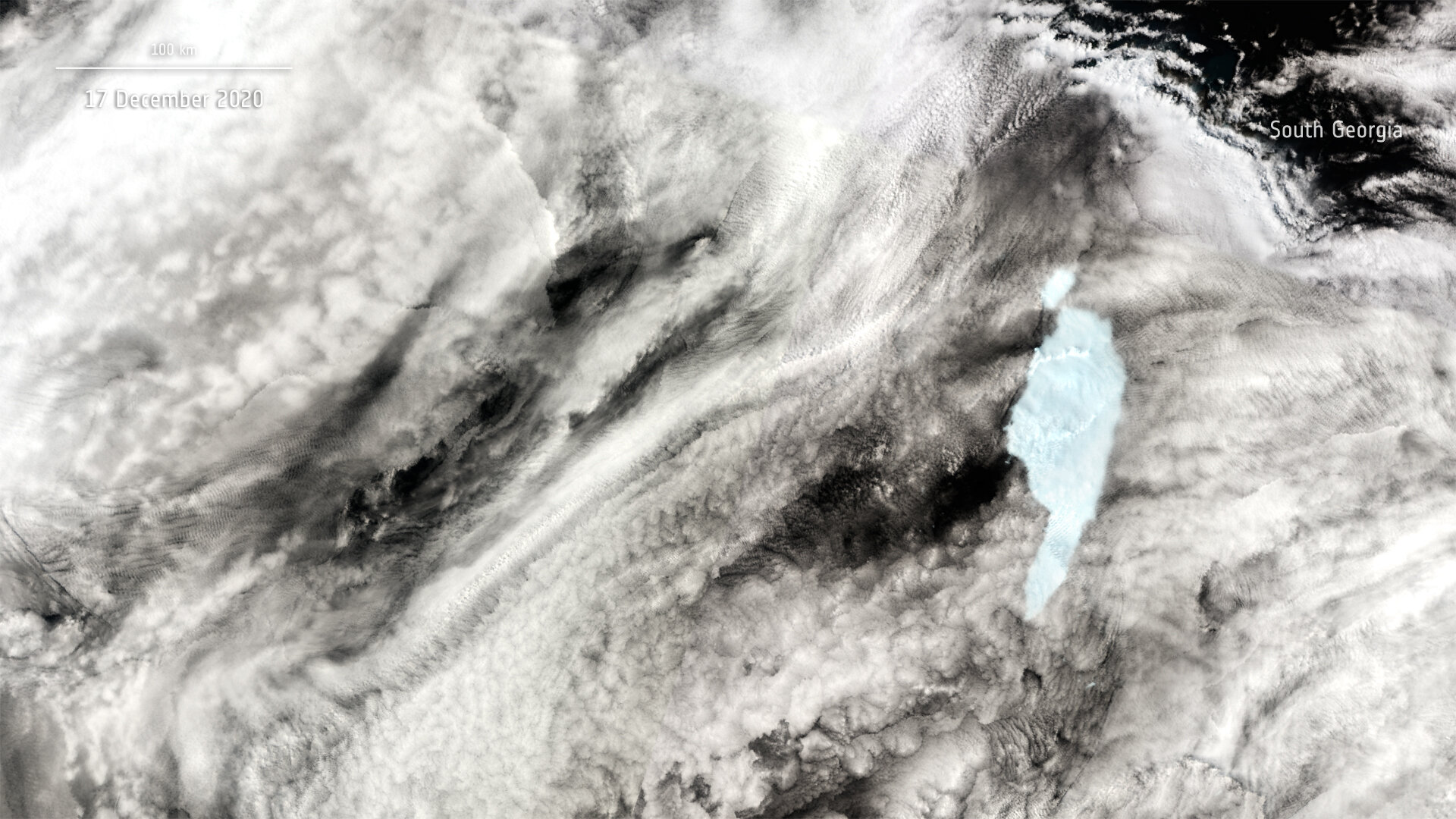
A big block of ice has damaged off the northern tip of the A-68A iceberg as seen in new photographs captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-Three mission.
Satellite missions have been used to trace the A-68A berg on its journey since 2017, when it broke off the Larsen C ice shelf in Antarctica. Over the previous weeks, the A-68A iceberg has drifted alarmingly near the distant island of South Georgia, the place scientists feared that the iceberg may floor within the shallow waters offshore and threaten wildlife.
A-68A iceberg breaks off
New satellite tv for pc photographs revealed yesterday that the iceberg has spun round in a clockwise path, transferring one finish of the berg nearer to the shelf and into shallow waters. In doing so, the berg may have scraped the seafloor, measuring lower than 200 m deep, inflicting an unlimited block of ice to snap off the iceberg’s northern tip.The new chunk of ice is round 18 km lengthy and roughly 140 sq km, across the identical measurement as Seville, Spain, and may be seen indifferent from the primary A-68A iceberg within the photographs. Despite its small look within the photographs, the brand new piece of ice is so massive it would most definitely be named A-68D by the US National Ice Centre within the coming days. Two different chunks of ice that beforehand broke off have been named A-68B and A-68C.
A-68A’s place on 17 December
The essential A-68A iceberg is now roughly 3700 sq km with a size of round 135 km. Having misplaced many different items of ice over the previous weeks, A-68A has now misplaced its title because the world’s largest iceberg. First place now passes onto the A-23A iceberg, which is presently caught within the Weddell Sea, with a measurement of nearly 4000 sq km.It remains to be unclear the place the primary A-68A iceberg will now journey. Carried by currents, it may proceed its journey across the island of South Georgia as many different earlier icebergs have accomplished prior to now, transferring in a southeast path, earlier than turning north.The map under reveals the completely different positions of the berg over the course of its three-year journey. The map highlights that in its first two years of freedom A-68 drifted slowly, impeded by sea ice. But because it moved in comparatively open waters, the tempo of the iceberg elevated.
A-68A’s journey
The map additionally contains historic iceberg tracks, primarily based on information from a quantity of satellites together with ESA’s ERS-1 and ERS-2 as half of the Antarctic Iceberg Tracking Database, and reveals that A-68A is following this well-trodden path.Satellite missions are getting used to trace the berg on its journey over the previous three years. The Sentinel-1 radar mission particularly, with its capacity to see by way of clouds and the darkish, has been instrumental in mapping the polar areas in winter.For the total A-68A narrative, click on right here.
Like
Thank you for liking
You have already preferred this web page, you possibly can solely prefer it as soon as!
Source link